With the new wave of technologies such as Big Data, Cloud, IoT, Mobile computing, there has been a significant surge in data generation, and consequently, storing, processing and sharing of data in huge amount. The rising need of huge storage space coupled with the fact that 2D NAND architecture has reached its physical limits, has led to the product manufacturers shifting from the traditional 2D NAND Technology towards 3D NAND.
Memory cells are stacked upon each other vertically in the 3D NAND, thereby increasing the capacity, storage density, reliability and lowering the cost per gigabyte and power consumption.
The three types of 3D NAND Flash Technology include:
- Single Level Cell (SLC) stores one bit per cell, has highest endurance.
- Multiple Level Cell (MLC) stores multiple bit per cell, has lower endurance than SLC.
- Triple Level Cell (TLC) stores three bits per cell, has the lowest endurance.
3D NAND creates a space for future increase up to 256GB to 512GB which was limited only till 128GB in case of 2D NAND.
Complexities involved during the process of implementation of 3D NAND resulted in the rise in cost of manufacturing initially. However, over the past five years, there has been progress, and manufacturers and material suppliers have been able to fill the gap to fulfil the rising demand of huge storage space.
Although 3D NAND is dedicated to provide higher capacities products at a lower price, there are few challenges that needs to be addressed for its smooth implementation. These include the following:
- Increase in the height of a multi-layered stack results in more complexities in achieving consistent deposition rate from top till the bottom of the array.
- The speed of the device can slow down because of slow movement of the electrons within the stack.
- Involvement of more and more memory cells means more chances of contamination so measures should be taken to reduce impurity.
Use of new innovative materials and techniques having higher resistance and stability should be used to overcome such issues.
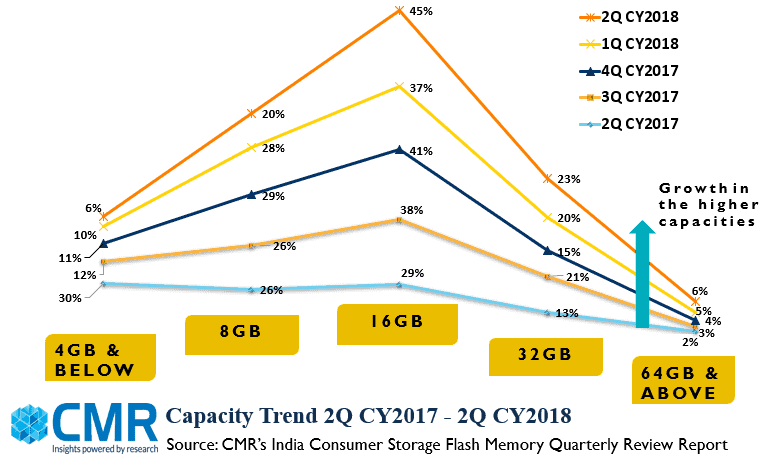
Effect of 3D NAND implementation in manufacturing process is clearly visible in the India consumer storage market comprising Micro SD, SD Card and Pen Drives. The overall market is witnessing a significant shift towards 32 GB capacity and is expected to shift further towards higher capacities due to their availability at low cost. However,16GB capacity is still the most favoured one.
Samsung was the first manufacturer to produce vertical 3D NAND in 2013. Other 3D NAND manufacturers include Intel, Micron, Toshiba, S K Hynix, and SanDisk.
Solid State Drives (SSD) form major part of the storage device ecosystem and have been used as a main storage for laptops, PC etc. along with the HDDs. However, SSDs have always been pricey relatively to the per gigabyte cost of a regular HDD. Use of 3D Vertical NAND technology have helped SSD manufacturers in reducing the manufacturing cost per bit, maximising the chip capacity and thereby finally producing a low priced SSD with less noise and less power consumption.
3D NAND will help SSD in giving tough competition to the HDD as it can be easily available in small size that an average HDD, having shock resistance. Consumers looking to upgrade their PC or Laptop to an SSD can easily go for it. Consumer devices like tablets, smartphones etc will soon be offering same storage capacity as that of PCs and laptop as of result of this technology. There will be no storage scarcity with respect to storing HD photos, videos, movies etc. in our smartphone and other devices.
India Consumer SSD market will grow at a constant rate as manufacturers have started embracing 3D NAND technology thereby overcoming the price barrier. However its possible only when they focus to overcome the challenges attached to it.